Category Archives: Marine Equipment Testing
Need your ‘Marine Equipment’ be tested and certified?
We provide testing and certification services at Istanbul Technical University Marine Equipment Test Center (METC)
In all project test phases, starting from requirements to verification tests, unit tests, integration tests, environment tests, and final/acceptance testing, we can support you. We can plan and test mechanical products, electrical equipment and devices, composite and innovative materials/alloys, Hazardous Materials (HAZ-MAT) packaging, medical equipment, an many other type of products developed in field use in dynamic environments.
We provide test and evaluation training
at your location
or
at Istanbul Technical University (ITU) Maritime Faculty (ITMF) Campus
in Tuzla, Istanbul.

Our test center, Marine Equipment Test Center (METC) is located in Tuzla, Istanbul. METC provides accredited services for testing prototypes for harsh environments, such as temperature, humidity, drop, tensite, loading, inside pressure, corrosion, etc. We perform tests according to ISO 17025. We are experienced in developing proposals with verification and validation activities. Whether you are developing a device or a piece of software, we are experienced in developing test plans, procedures, and reports. In short we manage your test project wşth a due diligence.
- Testing of Hazardous Material (HAZ-MAT) packages for transportation
(Product testing per ADR Agreement) - Testing of Marine Equipment and Life Saving Equipment (LSA) (per IMO LSA Code)
- Short Training Courses on Test Planning and Documents, Test Standarts, Testing and Test Management
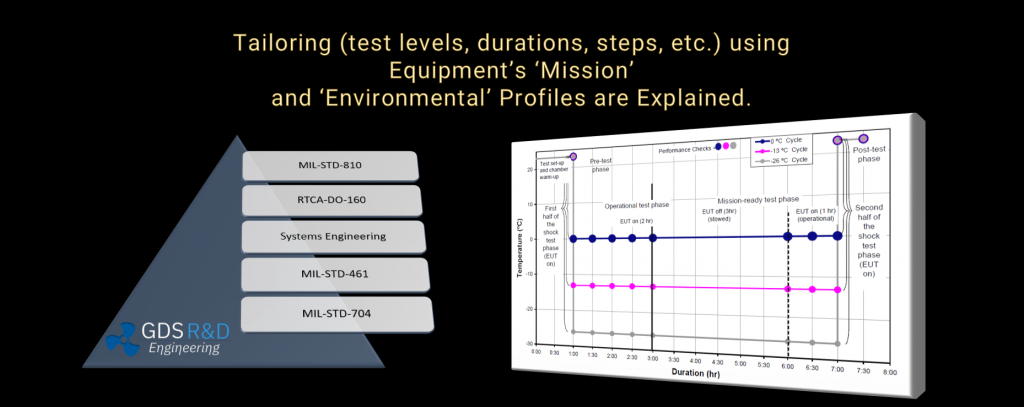
(Training on MIL-STD-810H, RTCA-DO-160G, MIL-STD-461G, and other standards) - Vibration and Shock testing.
- Testing of military equipment per MIL-STD-810H (DOD/military test standards)
- Testing of equipment per RTCA-DO-160G (aviation test standards per EASA / SHGM)
- Tensile testing of metals, composites, alloys, straps, etc.
- Surface roughness
- Corrosion testing (MIL-STD-810H, RTCA-DO-160, and including the ASTM sample tests)
- Static load testing

The manager of the METC facility, Dr. Ismail Cicek, have long years of testing experties since 2000s. MIL-STD-810G, RTCA-DO-160, ADR agreement for testing of hazardous packaging materias for transportation, Life Saving Appliances (LSA) Code are some of the standarts that we are experienced with and we do have the labratory with test infrastructure. Recently, testing of big HAZMAT packages (Internmediate Bulk Container, IBC) capability was added.

Additionally, some verification activities can be done using analysis techniques. We can perform Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), Finite Element Analysis (FEA), Fluid-Structure Interference (FSI) analysis in design stage for design verification and optimization.
GLOBAL DYNAMIC SYSTEMS (GDS)
TRAINING COURSES
Worldwide, Online, for ‘Groups’ or ‘Individuals’
Training on
MIL-STD-810H
ENVIRONMENTAL TESTING
“IPS/ILS, Reliability & Systems Engineering”
Certification Training
Training on
EMI/EMC Testing
(per RTCA-DO-160 & MIL-STD-461)
Training on
Vibration and Shock
Testing
Training on
Systems Engineering
(DoD/FAA/NASA/EASA)
Training on
RTCA-DO-160G
ENVIRONMENTAL TESTING
Training on
MIL-STD-461G EMI/EMC Testing
(incl. MIL-STD-464)
Training on
Requirements Management
(FAA/EASA/US DoD/NASA)
Training on
MIL-STD-704F
Aircraft Electrical Interface